How do electric buses work?
 Key components of an electric bus
Key components of an electric bus
High-capacity batteries
Electric buses are equipped with high-capacity batteries that store the energy needed to power the electric motor. These batteries are generally advanced lithium-ion batteries, capable of storing a large amount of energy and gradually releasing it to propel the vehicle. Modern electric buses are designed with modular battery systems, making it easy to adjust capacity to the specific needs of each route.
Electric motor
Unlike traditional buses with internal combustion engines, electric buses use an electric motor to generate mechanical power. Electric motors are generally located at the rear of the bus, close to the wheels, allowing power to be transmitted directly to the drive wheels. Electric motors offer high energy efficiency and rapid acceleration, which contribute to the overall performance of the electric bus.
The different components of an electric bus
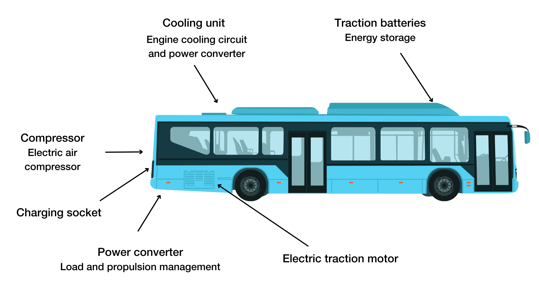
The electric propulsion system
Recharging batteries
Electric buses can be recharged in a number of ways. They can be connected to slow-charging stations during extended periods of parking, such as at bus terminals or depots. In addition, electric buses can also be fitted with fast-charging systems using pantographs. These pantographs enable rapid charging at bus stops, where batteries can be recharged in just a few minutes.
Energy recovery
A key advantage of electric buses is their ability to recover kinetic energy during braking. Electric buses are equipped with regenerative braking systems, which convert kinetic energy into electrical energy, recharging the bus's batteries. This feature optimises the bus's range and reduces overall energy consumption.
The advantages of electric buses
Reducing emissions
Electric buses help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and atmospheric pollution. As electric buses are not dependent on fossil fuels, they produce no direct exhaust emissions. This helps to improve air quality in urban areas and combat climate change by reducing CO2 emissions.
Lower operating costs
Although electric buses require a higher initial investment due to the cost of batteries and recharging infrastructure, they offer lower long-term operating costs. Electric buses have lower maintenance costs thanks to fewer moving parts and less wear and tear on the electric motor. In addition, fuel costs are considerably reduced because electricity is generally cheaper than traditional fuels.
Electric buses represent a major advance in sustainable urban transport. Their operation is based on key components such as high-capacity batteries and electric motors, offering a clean and efficient alternative to traditional internal combustion buses. Thanks to their electric propulsion system and their environmental and economic benefits, electric buses help to improve air quality, reduce greenhouse gas emissions and optimise operating costs. By investing in this emerging technology, cities can move towards more sustainable urban mobility and create a better future for generations to come.

%20(1).png)

